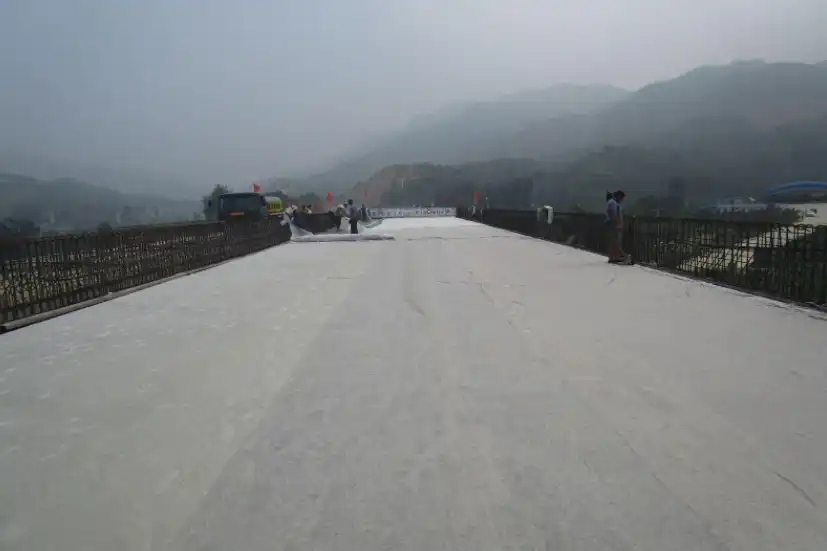
Road maintenance geotextile (polyester geotextile, non-woven geotextile), also known as geotextile, is a material composed of chemical fibers that are tested for water absorption through needle tying or spinning. The product is in the form of fabric, with a general spacing of 4-6 meters and a length of 50-100m. In brief, geotextiles are divided into woven geotextiles and non-woven geotextiles.
The geotextile for road maintenance mainly has the following characteristics
1. Geotextiles for road maintenance are widely used for the improvement of asphalt pavement, concrete pavement, and foundation. Both compulsory and soft road surfaces can be used, which can reduce engineering costs, increase service life, and avoid cracks on the reflective surface of the road compared to traditional road surfaces.
2. The pavement maintenance geotextile is suitable for thin and thick thickness, and is easy to blend with asphalt pavement. After blending with adhesive layer oil, it produces an isolation layer, which has moisture-proof and thermal insulation effects.
3. Road maintenance geotextile has light quality and high toughness. The compressive strength is ≥ 8 KN/m, and the tensile strength is 40-60%, fully meeting the technical standards for geotextiles in JTJ/T019-98 "Technical Specification for Stress of Highway Geosynthetic Materials".
4. The surface of the pavement maintenance geotextile is not smooth and is not easy to roll. When paving, the surface should be treated with a rough surface facing downwards to increase friction resistance, improve overall surface adhesion, and avoid being rolled over or damaged by wheels during construction. Together, it can suppress the problem of vehicle and asphalt paver deviation on the fabric.
5. The geotextile for road maintenance has the ability to block ultraviolet rays, withstand low temperature freezing, resist corrosion, and resist biological damage.
6. The pavement maintenance geotextile is easy to construct and has good application effects. The fiber filaments of general geotextiles are easily driven by vehicle tires, causing wire hanging, and in severe cases, they may even be rolled over, causing displacement and structural damage to the geotextile.
.png)
.png)